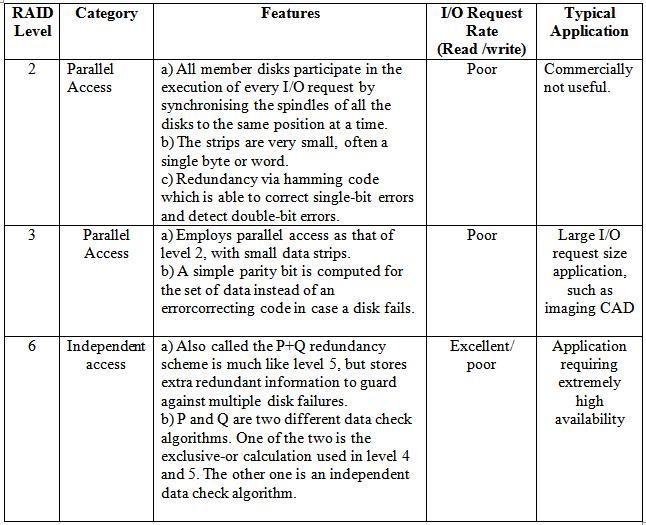
In RAID levels, explain the features of those levels which have poor I/O request rate (read/write) 5m Dec2005
Redundancy of data industrial standard, which exists for multiple-disk database schemes, is termed as RAID, i.e., Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
The basic characteristics of RAID disks are:
- Operating system considers the physical disks as a single logical drive.
- Data is distributed across the physical disks.
- In case of failure of a disk, the redundant information (for example, the parity bit) kept on redundant disks is used to recover the data.
|
RAID Level |
Category |
Features |
I/O Request Rate (Read /write) |
Typical Application |
|
2 |
Parallel Access | a) All member disks participate in the execution of every I/O request by synchronising the spindles of all the disks to the same position at a time.
b) The strips are very small, often a single byte or word. c) Redundancy via hamming code which is able to correct single-bit errors and detect double-bit errors. |
Poor |
Commercially not useful. |
|
3 |
Parallel Access
|
a) Employs parallel access as that of level 2, with small data strips.
b) A simple parity bit is computed for the set of data instead of an errorcorrecting code in case a disk fails.
|
Poor |
Large I/O request size application, such as imaging CAD |
|
6 |
Independent access
|
a) Also called the P+Q redundancy scheme is much like level 5, but stores extra redundant information to guard against multiple disk failures.
b) P and Q are two different data check algorithms. One of the two is the exclusive-or calculation used in level 4 and 5. The other one is an independent data check algorithm.
|
Excellent/ poor |
Application requiring extremely high availability |