If you have just started learning Assembly language programming, here is a example Assembly program explained so that you can understand the very basic terminology before you write more complex Assembly Applications. First Assembly program simply prints a text message “Hello World” on Screen.
[codesyntax lang=”asm”]
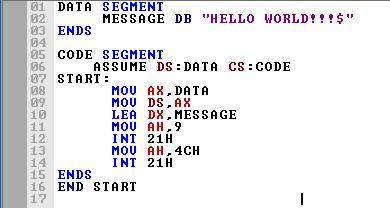
DATA SEGMENT
MESSAGE DB "HELLO WORLD!!!$"
ENDS
CODE SEGMENT
ASSUME DS:DATA CS:CODE
START:
MOV AX,DATA
MOV DS,AX
LEA DX,MESSAGE
MOV AH,9
INT 21H
MOV AH,4CH
INT 21H
ENDS
END START
[/codesyntax]
In this Assembly Language Programming, A single program is divided into four Segments which are 1. Data Segment, 2. Code Segment, 3. Stack Segment, and 4. Extra Segment. Now, from these one is compulsory i.e. Code Segment if at all you don’t need variable(s) for your program.if you need variable(s) for your program you will need two Segments i.e. Code Segment and Data Segment.
First Line – DATA SEGMENT
DATA SEGMENT is the starting point of the Data Segment in a Program and DATA is the name given to this segment and SEGMENT is the keyword for defining Segments, Where we can declare our variables.
Next Line – MESSAGE DB “HELLO WORLD!!!$”
MESSAGE is the variable name given to a Data Type (Size) that is DB. DB stands for Define Byte and is of One byte (8 bits). In Assembly language programs, variables are defined by Data Size not its Type. Character need One Byte so to store Character or String we need DB only that don’t mean DB can’t hold number or numerical value. The string is given in double quotes. $ is used as NULL character in C programming, So that compiler can understand where to STOP.
Next Line – DATA ENDS
DATA ENDS is the End point of the Data Segment in a Program. We can write just ENDS But to differentiate the end of which segment it is of which we have to write the same name given to the Data Segment.
Next Line – CODE SEGMENT
CODE SEGMENT is the starting point of the Code Segment in a Program and CODE is the name given to this segment and SEGMENT is the keyword for defining Segments, Where we can write the coding of the program.
Next Line – ASSUME DS:DATA CS:CODE
In this Assembly Language Programming, their are Different Registers present for Different Purpose So we have to assume DATA is the name given to Data Segment register and CODE is the name given to Code Segment register (SS,ES are used in the same way as CS,DS )
Next Line – START:
START is the label used to show the starting point of the code which is written in the Code Segment. : is used to define a label as in C programming.
Next Line – MOV AX,DATA
MOV DS,AX
After Assuming DATA and CODE Segment, Still it is compulsory to initialize Data Segment to DS register. MOV is a keyword to move the second element into the first element. But we cannot move DATA Directly to DS due to MOV commands restriction, Hence we move DATA to AX and then from AX to DS. AX is the first and most important register in the ALU unit. This part is also called INITIALIZATION OF DATA SEGMENT and It is important so that the Data elements or variables in the DATA Segment are made accessable. Other Segments are not needed to be initialized, Only assuming is enhalf.
Next Line – LEA DX,MESSAGE
MOV AH,9
INT 21H
The above three line code is used to print the string inside the MESSAGE variable. LEA stands for Load Effective Address which is used to assign Address of variable to DX register (The same can be written like this also MOV DX,OFFSET MESSAGE both mean the same). To do input and output in Assembly Language we use Interrupts. Standard Input and Standard Output related Interupts are found in INT 21H which is also called as DOS interrupt. It works with the value of AH register, If the Value is 9 or 9h or 9H (all means the same), That means PRINT the string whos Address is Loaded in DX register.
Next Line – MOV AH,4CH
INT 21H
The above two line code is used to exit to dos or exit to operating system. Standard Input and Standard Output related Interupts are found in INT 21H which is also called as DOS interrupt. It works with the value of AH register, If the Value is 4ch, That means Return to Operating System or DOS which is the End of the program.
Next Line – CODE ENDS
CODE ENDS is the End point of the Code Segment in a Program. We can write just ENDS But to differentiate the end of which segment it is of which we have to write the same name given to the Code Segment.
Last Line – END START
END START is the end of the label used to show the ending point of the code which is written in the Code Segment.
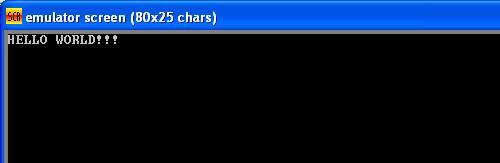
Execution of program explanation – Hello World
First save the program with HelloWorld.asm filename. No Space is allowed in the name of the Program File and extension as .asm (dot asm because it’s a Assembly language program). The written Program has to be complied and Run by clicking on the RUN button on the top. The Program with No Errors will only run and could show you the desired output. Just see the screenshots below.
Note :- In this Assembly Language Programming, We have Com format and EXE format. We are Learning in EXE format only which simple then COM format to understand and Write. We can write the program in lower or upper case, But i prepare Upper Case. (this program are executed on emu8086 emulator software)
Screen Shots :-